Neuroscience of Creativity: How Your Brain Generates Ideas
Ever wonder why some days ideas flow like a river and other days your mind feels dry? It all comes down to what’s happening inside your head. The brain has a built‑in system for mixing old thoughts and new twists. Understanding that system can help you spark ideas on demand.
What Happens in the Brain When You’re Creative
When you tap into creativity, two main networks light up: the default mode network (DMN) and the executive control network (ECN). The DMN runs in the background, linking memories, day‑dreams, and random thoughts. The ECN steps in to focus, shape, and test those raw ideas. When the two talk together, you get that "aha!" moment.
Neuroscientists have spotted bursts of dopamine—your brain’s reward chemical—right before a breakthrough. Dopamine makes you feel good about the new connection, so you keep exploring it. At the same time, the brain reduces activity in the "filter" part (the inferior frontal gyrus), which normally stops weird ideas. Less filtering = more wild ideas.
Studies using fMRI show that people who practice creative arts therapies have stronger connections between these networks. That’s why art, music, or dance can train your brain to be more flexible. Even simple activities like doodling or humming can give the DMN a gentle nudge.
Simple Ways to Jump‑Start Your Creative Brain
1. Change your scenery. A short walk, a new coffee shop, or even rearranging a desk can shift the DMN into gear. The new visual cues act like fresh fuel for ideas.
2. Use a 10‑minute timer. Set a timer and let yourself write, sketch, or brainstorm without judgment. The time pressure keeps the ECN focused while the DMN runs free.
3. Play with constraints. Pick a random word, limit yourself to three colors, or write a story in 100 words. Constraints force the brain to combine old stuff in new ways.
4. Practice mindfulness. A few minutes of breathing helps lower stress hormones that can choke creativity. When you’re calm, dopamine flows more easily.
5. Mix up the senses. Listen to an unfamiliar genre, try a new recipe, or feel different textures. Multisensory input feeds the DMN with varied material to remix.
Implementing any of these tricks doesn’t need a lab or fancy gear—just a bit of curiosity. Over time, you’ll notice the brain getting quicker at making connections, and the "blank page" feeling will fade.
So next time you need a fresh idea, remember: it’s not magic, it’s a brain process you can nudge. Give the networks a reason to talk, and let the ideas roll in.
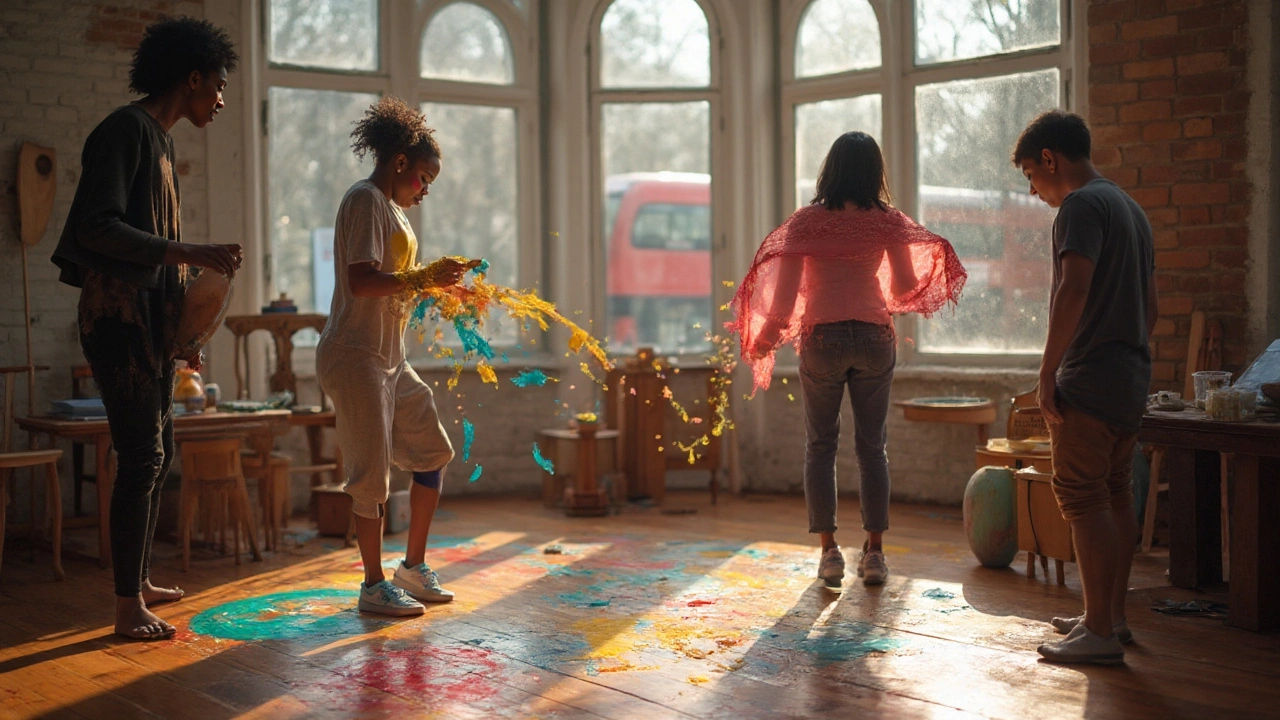
The Science Behind Creative Arts Therapies: Brain Mechanisms, Evidence, and Real-World Results
Sep 22 2025 / TherapiesHow creative arts therapies change the brain and body: mechanisms, evidence, what sessions look like, who they help, and how to start-explained clearly and concisely.
VIEW MORE